Type 2 Inflammation
The Role of IL-4 and IL-13 in CSU Pathogenesis
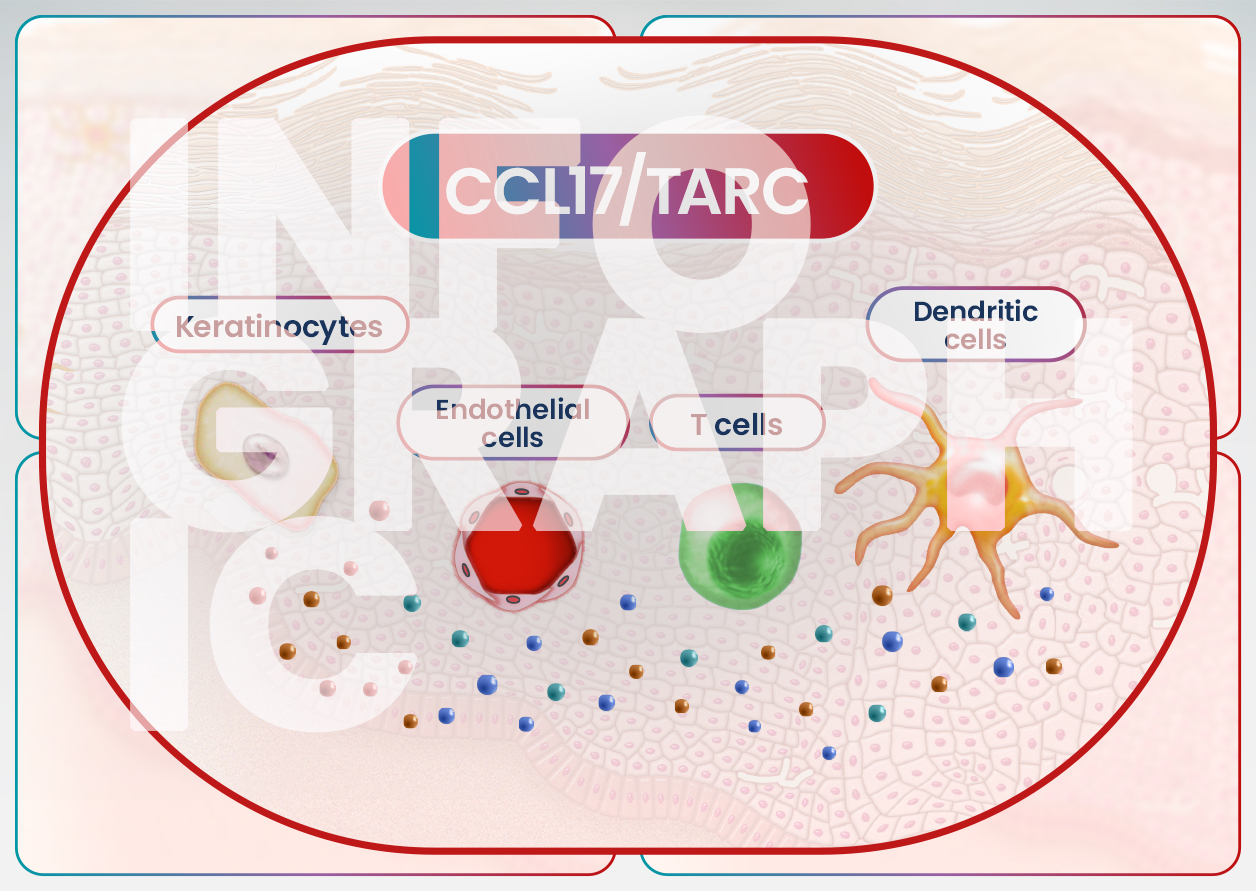
Dive into the complex pathophysiology of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), where mast cell degranulation drives the hallmark signs and symptoms. This interactive infographic elucidates how key type 2 cytokines, specifically IL-4 and IL-13, contribute to mast cell activation, immune cell trafficking into the skin, and neuronal sensitization in CSU, which ultimately leads to the release of mediators like histamine that cause wheals, angioedema, and itch.
Learning objectives
- Explain the central role of mast cell activation and degranulation in CSU pathophysiology
- Summarize the specific mechanisms by which type 2 cytokines, IL-4 and IL-13, influence mast cell activation, immune cell recruitment to the skin, and neuronal sensitization in CSU pathophysiology
Tags
MAT-GLB-2600107 – 1.0 – 01/2026