Dermatology
Barrier disruption in AD and the development of environmental and food allergies
Dr. Casale discusses the critical role of barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis
Learning objectives
- Comprehend the role of barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis, identifying its primary causes, such as genetic mutations, and secondary causes, like inflammatory cytokines and physical damage
- Recognize the theory of how barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis may lead to sensitization to environmental allergens
Description
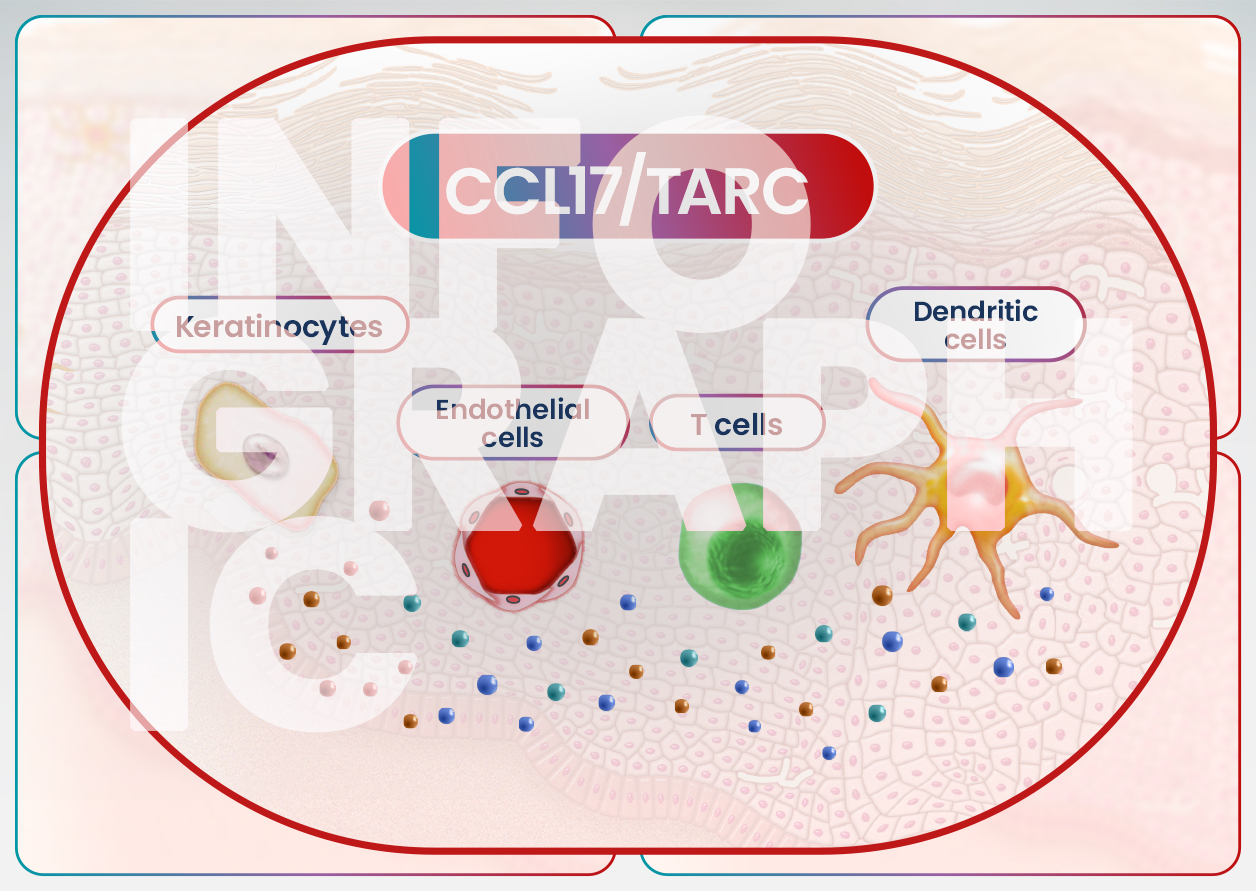
The video explains, barrier disruption is a critical component of AD, whether due to genetic mutations like filaggrin gene mutation or secondary factors such as inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. These cytokines directly damage the barrier, and scratching exacerbates this damage. Barrier disruption in AD may lead to sensitization to environmental allergens.
Tags
MAT-GLB-2403268- 1.0 - 07/2024